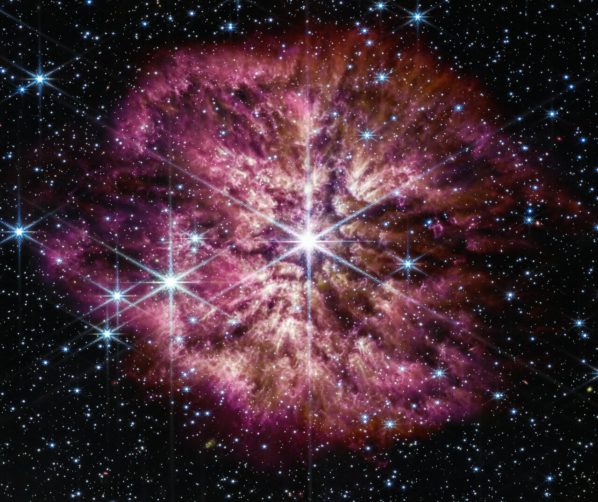
What Is a Wolf-Rayet Star?
Uncover what is a Wolf-Rayet star. Explore their extreme temperatures, massive scale, and significant role in shaping the galactic landscape. Join us in unraveling the mysteries of these celestial giants.
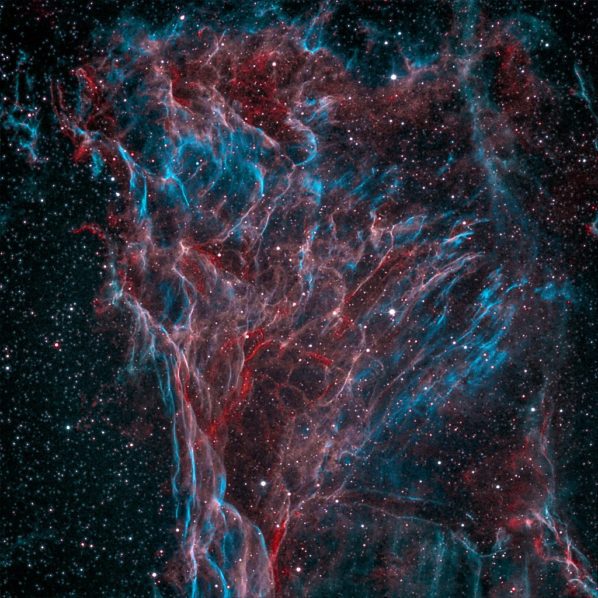
Pickering’s Triangle: Unveiling the Beauty of Stellar Remnants
Discover Pickering's Triangle: a stunning cosmic remnant within the Veil Nebula, offering a mesmerizing glimpse into the aftermath of a supernova explosion in Cygnus.
NGC 2336 – A Unique Barred Spiral Galaxy
NGC 2336: a distant barred spiral galaxy boasting a luminous ring, central bar, and a powerful black hole at its core. Explore its cosmic wonders.
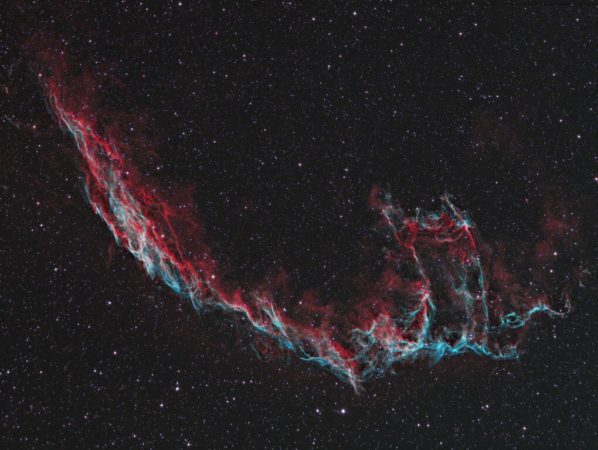
NGC 6992: Brightest Part of the Eastern Veil Nebula
Uncover the mesmerizing beauty of NGC 6992, a captivating segment within the Eastern Veil Nebula. Journey 2400 light-years away to explore this cosmic wonder born from a supernova's ancient explosion.
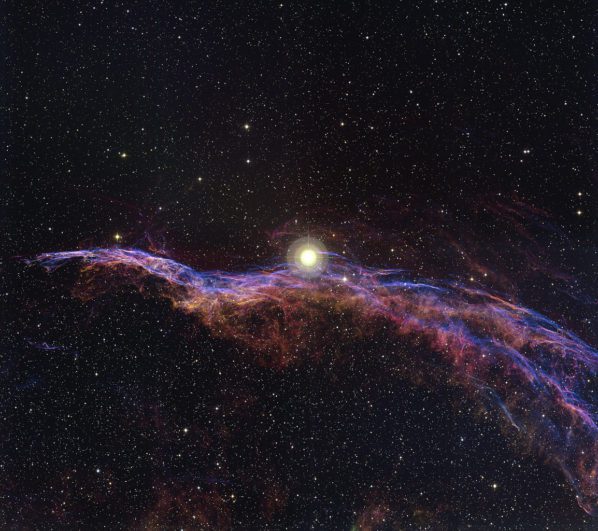
NGC 6960 – The Witch’s Broom Nebula
The Witch's Broom Nebula (NGC 6960), in Cygnus, 2400 light-years away, is a striking, young supernova remnant. Its beauty captures scientists and stargazers, offering insights into cosmic evolution.
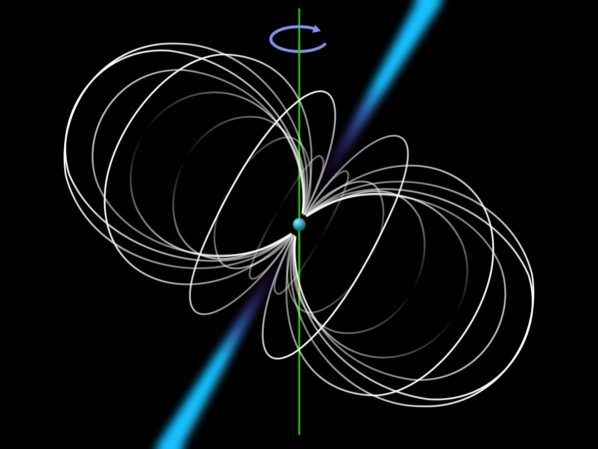
A Pulsar With Planets
Pulsars emit deadly radiation, disintegrating DNA and making them dangerous. Surprisingly, some have planets orbiting them, defying current theories.
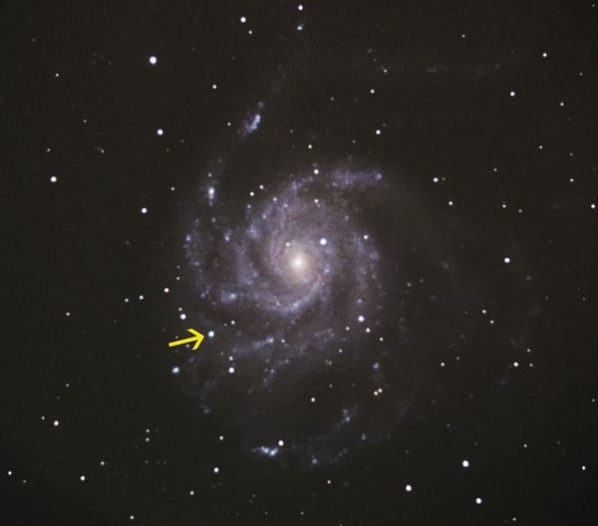
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for September 2011
This month you can witness a supernova with just binoculars or a small telescope. The supernova is called SN 2011fe and has been discovered by astronomers on August 24 within hours of its explosion. It is located within the Messier 101 galaxy 23 million light-years away in the constellation of Ursa Major.
Astronomy Picture of the Week – Supernova Bubble Resembling Holiday Ornament
This image was made by combining data from two of NASA's Great Observatories: the Hubble Space Telescope and the Chandra X-ray Observatory. The supernova remnant, cataloged as SNR 0509-67.5, is the result of a type Ia supernova. It is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a small galaxy about 160,000 light-years from Earth.
Astronomy Picture of the Week – The Cat’s Eye Nebula
This detailed view of the so-called Cat’s Eye Nebula was taken by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. The nebula, formally cataloged as NGC 6543, was one of the first planetary nebulae to be discovered and is one of the most complex. Observations suggest the star ejected its mass in a series of pulses at 1,500-year intervals. This created dust shells, each of which contain as much mass as all of the planets in our solar system combined. These concentric shells make a layered, onion-skin structure around the dying star. Image Credit: NASA, ESA, HEIC, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
Astronomy Picture of the Week – The Colorful Demise of a Sun-Like Star
This image, taken by the Hubble Space Telescope, shows the colorful demise of a Sun-like star. The star is ending its life by casting off its outer layers of gas, which formed a cocoon around the star’s remaining core. Ultraviolet light from the dying star makes the material glow. The burned-out star, called a white dwarf, is the white dot in the center. It is one of the hottest known white dwarfs, with a surface temperature of nearly 200,000 degrees Celsius. The nebula is called NGC 2440 and lies about 4,000 light-years from Earth in the direction of the constellation Puppis. Image credit: NASA, ESA, and K. Noll (STScI)
Astronomy Picture of the Week – Helix Nebula
This eerie picture captured by the Spitzer Space Telescope shows the Helix Nebula, also known as NGC 7293. It is located 700 light-years away in the constellation of Aquarius. The two light-year diameter shroud of dust and gas around a central white dwarf is the result of the final stages in the evolution of a sun-like star. Dust particles are what makes this cosmic eye look red. Image Credit & Copyright: NASA, JPL-Caltech, Kate Su (Steward Obs., U. Arizona), et al.
Astronomy Picture of the Week – Distant Nebula
This nebula, designated as N 49 or DEM L 190, looks like puffs of smoke or sparks from a fireworks display. It is one of the most distant nebulae ever observed, located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy orbiting the Milky Way. The nebula is the result of a large supernova, whose light should have reached Earth a few thousand years ago.