Astronomy
Embark on an astronomical journey. Explore the cosmos, study celestial objects, and unravel the mysteries of the universe through astronomy's fascinating realm.
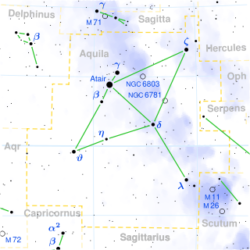
Aquila Constellation
Discover Aquila, the eagle, in Greek mythology. Explore its notable stars like Altair and Alshain, as well as intriguing deep-sky objects.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for July 2011
On the night of July 28 and 29 the Delta Aquarids will peak and we can expect about 20 meteors per hour that night. Some meteors can also be seen from July 18 to August 18. The meteor shower will seem to radiate from the constellation of Aquarius. This year the thin, crescent moon will be close to the meteor shower, but its light shouldn't interfere too much. The best viewing is usually to the east after midnight from a dark location.
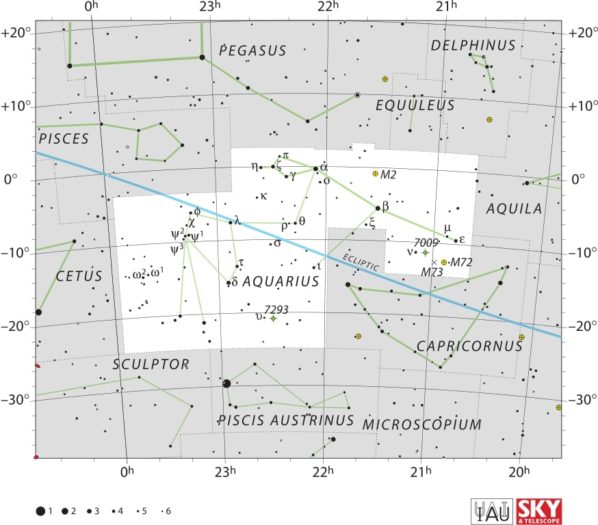
Aquarius Constellation
Explore the constellation Aquarius, the water-bearer. Discover its mythology, notable stars like Gliese 876, and captivating deep-sky objects like Messier 2.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for June 2011
On June 15 there will be a total lunar eclipse which will be visible throughout most of South America, Europe, Africa, Asia, and Australia. Unfortunately it will not be visible in North America. Here is a map with the exact areas where the lunar eclipse can be witnessed…
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for April 2011
The Lyrids are an average meteor shower with about 20 meteors per hour at their peak on April 21 and 22. These meteors can produce bright dust trails that last for several seconds. The shower is most spectacular during the peak on April 21 and 22, but some meteors can still be spotted from April 16 to 25. The meteors will be radiating from the constellation of Lyra after midnight.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for March 2011
This month, on the 20th, an equinox will occur. The Sun will shine directly on the equator and there will be nearly equal amounts of day and night throughout the world.
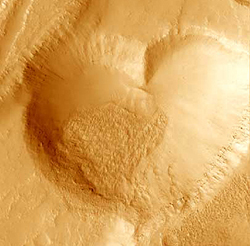
Cosmic Hearts
I hope you all had a happy Valentine's Day! :) Here are some pictures of cosmic hearts: A heart-shaped crater on Mars captured by the Mars Orbiter Camera onboard the Mars Global Surveyor. A heart-shaped Nebula, called W5, located 6000 light years away in the constellation of Cassiopeia.
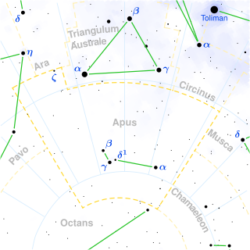
Apus Constellation
Apus is a faint constellation in the southern sky. Its name means “no feet” in Greek and it represents a bird-of-paradise, which were once believed to have no feet. It was one of the twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius in the late 16th century. The first known depiction of the constellation in a celestial atlas was in Johann Bayer’s Uranometria of 1603. Bird-of-Paradise after which the Apus constellation was named. Credit & Copyright: Roderick Eime. For more constellations see the Constellations Guide.
Introduction to Astronomy – Apparent magnitude
Yesterday I have used the term “apparent magnitude” in my article about the Antlia Constellation. Since some of you may be new to astronomy, I decided to start a new series of articles to introduce you to the topic. Each article of the series will focus on one scientific term used in astronomy. The series will not be a regular one: I will only write an article after using a complicated astronomy term that some of you would need me to explain. Definition The apparent magnitude (noted as m) of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth. Since the apparent brightness…
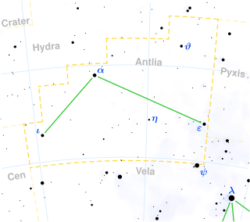
Antlia Constellation
Antlia is a constellation in the southern sky and therefore has been unknown to the ancient Greeks and Romans. Its name means “pump” and it specifically represents an air pump. It was created by the French astronomer Abbé Nicolas Louis de Lacaille, who created fourteen constellations for the southern sky to fill some of the faint regions. He originally named it Antlia pneumatica to commemorate the air pump invented by the French physicist Denis Papin. It was later adopted by the International Astronomical Union as one of the 88 modern constellations under the shortened name of Antlia. Main Stars and Deep Sky Objects The Antlia constellation has no bright stars.…
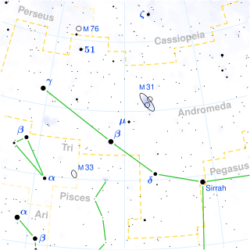
Andromeda Constellation
Andromeda is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. The Andromeda Galaxy is named after the constellation, as it appears within its boundaries.
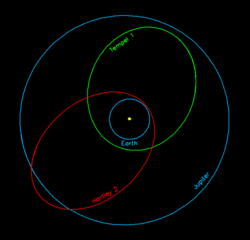
Hartley 2 Comet
Comet Hartley 2 has made it to the news recently: first because of the comet's flyby near Earth and then due to it being visited by the Deep Impact spacecraft.