Astronomy
Embark on an astronomical journey. Explore the cosmos, study celestial objects, and unravel the mysteries of the universe through astronomy's fascinating realm.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for November 2015
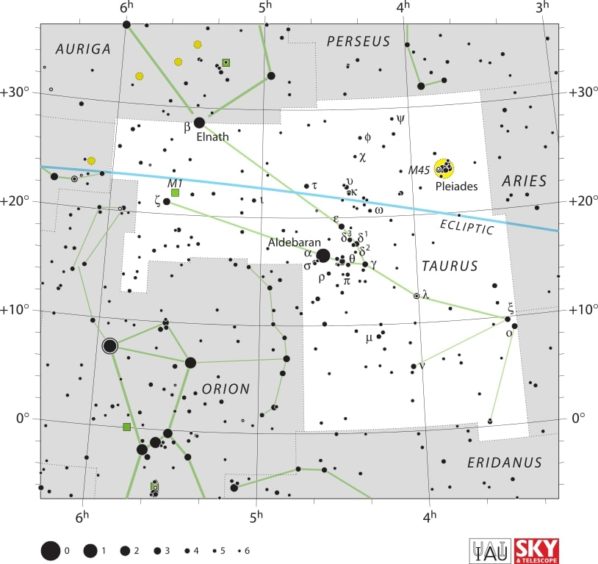
On the night of November 5 and 6 we will witness the peak of the Taurids meteor shower. It is a long-running minor meteor shower producing only about 5-10 meteors per hour at peak, while some meteors can also be seen from September 7 to December 10. However it is unusual in that it consists of two separate streams. The first is produced by dust grains left behind by Asteroid 2004 TG10. The second one is produced by debris left behind by Comet 2P Encke.
Light Pollution – What Is It and Why It’s Bad
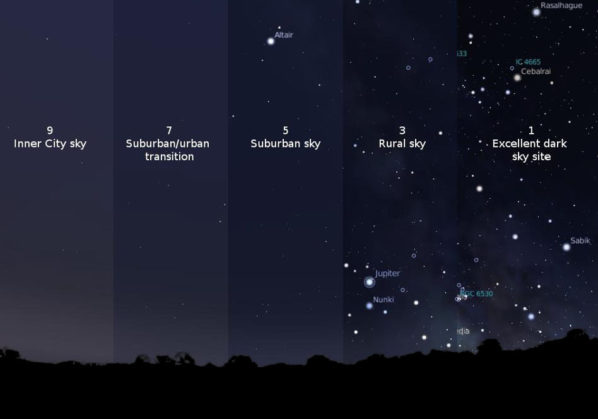
Light pollution stems from artificial lighting sources, impacting astronomy, ecosystems, and wildlife; mitigating strategies involve redesigning light sources.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for October 2015
On October 8 we will witness the Draconids meteor shower. It is a minor meteor shower producing only about 10 meteors per hour originating from dust grains left behind by comet 21P Giacobini-Zinner, which was first discovered in 1900. The Draconids is an unusual shower in that the best viewing is in the early evening instead of early morning like most other showers.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for September 2015
On September 13 there will be a partial solar eclipse. This type of eclipse occurs when the Moon covers only a part of the Sun, sometimes resembling a bite taken out of a cookie. For safety reasons, an eclipse should only be observed with a special solar filter or by looking at the Sun's reflection.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for August 2015
This month on the night of August 12 and 13 we will witness the Perseids meteor shower, which is one of the best meteor showers to observe, producing up to 60 meteors per hour at its peak. Some meteors can also be seen from July 17 to August 24. It originates from debris produced by comet Swift-Tuttle, which was discovered in 1862.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for July 2015
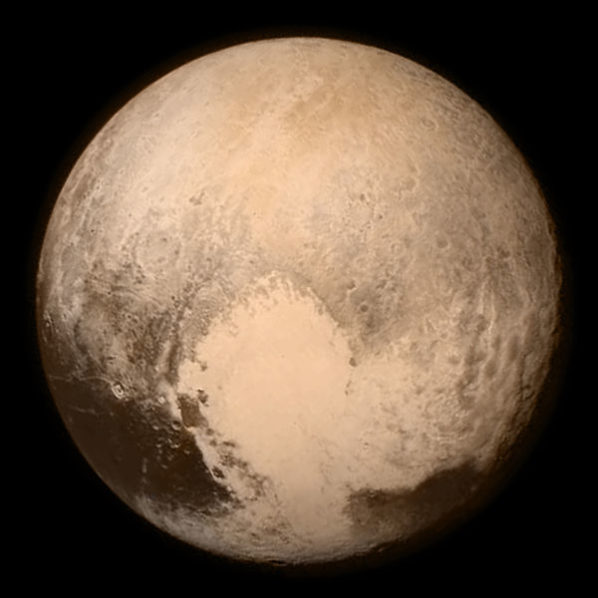
On July 14 NASA's New Horizons spacecraft is scheduled to arrive at Pluto after a nine and a half year journey. It was launched on January 19, 2006 and will be the first spacecraft to visit Pluto. New Horizons will give us our first close-up views of the dwarf planet and its moons.
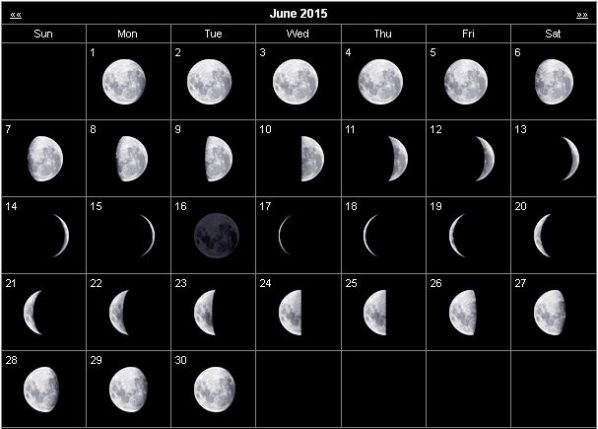
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for June 2015
On June 6 the planet Venus will be at greatest eastern elongation. Venus will reach greatest eastern elongation of 45.4 degrees from the Sun. This is the best time to view Venus because it will be at its highest point above the horizon in the evening sky. Look for the bright planet in the western sky after sunset.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for May 2015
Early this month, on the night of May 5th and 6th we will witness the peak of the Eta Aquarids meteor shower. It is an above average shower, capable of producing up to 60 meteors per hour at its peak. However most of the meteors can be seen in the Southern Hemisphere. For the rest of us in the Northern Hemisphere, the rate can reach about 30 meteors per hour.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for October 2014
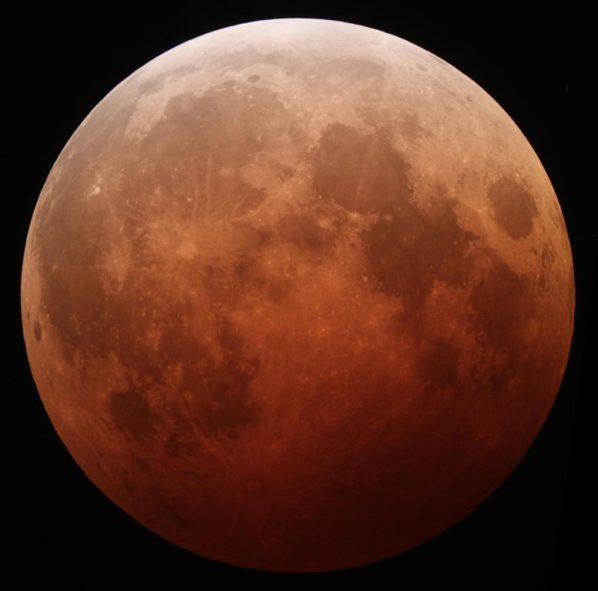
On October 8 we will witness a total lunar eclipse. Such an eclipse occurs when the Moon passes completely through the Earth's dark shadow, or umbra. The Moon will gradually get darker and then take on a rusty or blood red color. The eclipse will be visible throughout most of North America, South America, eastern Asia, and Australia.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for September 2014
This month will be rather uneventful when it comes to astronomical events except for the September equinox on the 23rd at 02:29 UTC. The Sun will shine directly on the equator and there will be nearly equal amounts of day and night throughout the world.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for August 2014
Tonight on August 12 and on the morning of August 13 the Perseids meteor shower will peak. It is one of the best meteor showers to observe, producing up to 60 meteors per hour at its peak. Some meteors can also be seen from from July 17 to August 24.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for July 2014
This month will be a rather quiet one, when it comes to astronomical events. However by the end of the month, on the night of July 28 and 29, the Delta Aquarids meteor shower will peak. It is an average shower that can produce up to 20 meteors per hour at its peak.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for June 2014
After a few months break, we are back with our monthly stargazing calendar series. On June 7 there will be a conjunction of the Moon and Mars. The two celestial bodies will get as close as two degrees of each other in the evening sky. The gibbous moon will be at magnitude -12.2 while Mars will be at magnitude -0.8.
Monthly Stargazing Calendar for January 2014
On January 5 the planet Jupiter was at Opposition. This means that the giant planet was at its closest approach to Earth and its face was fully illuminated by the Sun. The weeks preceding and following this event are the best time to view and photograph Jupiter and its moons.