Monthly Stargazing Calendar for March 2011
This month, on the 20th, an equinox will occur. The Sun will shine directly on the equator and there will be nearly equal amounts of day and night throughout the world.
Astronomy Picture of the Week – Polarized Star Light
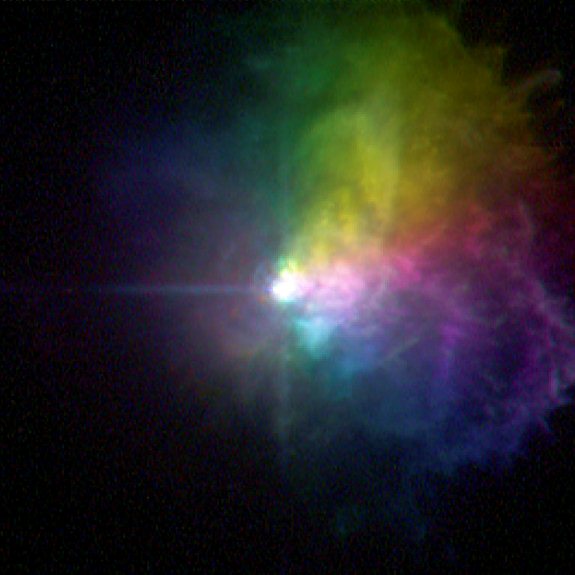
This picture taken by the Hubble Space Telescope shows the polarized light of the massive star VY Canis Majoris. Image Credit: NASA, ESA, and R. Humphreys (University of Minnesota)
Astronomy Picture of the Week – The Colorful Demise of a Sun-Like Star
This image, taken by the Hubble Space Telescope, shows the colorful demise of a Sun-like star. The star is ending its life by casting off its outer layers of gas, which formed a cocoon around the star’s remaining core. Ultraviolet light from the dying star makes the material glow. The burned-out star, called a white dwarf, is the white dot in the center. It is one of the hottest known white dwarfs, with a surface temperature of nearly 200,000 degrees Celsius. The nebula is called NGC 2440 and lies about 4,000 light-years from Earth in the direction of the constellation Puppis. Image credit: NASA, ESA, and K. Noll (STScI)
Astronomy Picture of the Week – NGC 1999 Nebula
This photo of nebula NGC 1999 was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope in December 1999. It is a good example of a reflection nebula. Just like fog around a street lamp, a reflection nebula shines only because a light source illuminates its dust and the nebula does not emit any visible light of its own. The main light source of this nebula is a recently formed star, visible in this photo near the center. This young star is cataloged as V380 Orionis, and its white color is due to its high surface temperature of about 10,000 degrees Celsius (nearly twice that of our own Sun). Its mass is estimated…
Astronomy Picture of the Week – Helix Nebula
This eerie picture captured by the Spitzer Space Telescope shows the Helix Nebula, also known as NGC 7293. It is located 700 light-years away in the constellation of Aquarius. The two light-year diameter shroud of dust and gas around a central white dwarf is the result of the final stages in the evolution of a sun-like star. Dust particles are what makes this cosmic eye look red. Image Credit & Copyright: NASA, JPL-Caltech, Kate Su (Steward Obs., U. Arizona), et al.
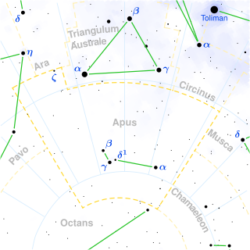
Apus Constellation
Apus is a faint constellation in the southern sky. Its name means “no feet” in Greek and it represents a bird-of-paradise, which were once believed to have no feet. It was one of the twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius in the late 16th century. The first known depiction of the constellation in a celestial atlas was in Johann Bayer’s Uranometria of 1603. Bird-of-Paradise after which the Apus constellation was named. Credit & Copyright: Roderick Eime. For more constellations see the Constellations Guide.
Introduction to Astronomy – Apparent magnitude
Yesterday I have used the term “apparent magnitude” in my article about the Antlia Constellation. Since some of you may be new to astronomy, I decided to start a new series of articles to introduce you to the topic. Each article of the series will focus on one scientific term used in astronomy. The series will not be a regular one: I will only write an article after using a complicated astronomy term that some of you would need me to explain. Definition The apparent magnitude (noted as m) of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth. Since the apparent brightness…
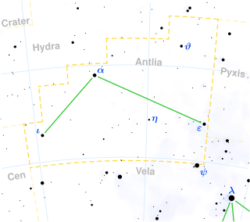
Antlia Constellation
Antlia is a constellation in the southern sky and therefore has been unknown to the ancient Greeks and Romans. Its name means “pump” and it specifically represents an air pump. It was created by the French astronomer Abbé Nicolas Louis de Lacaille, who created fourteen constellations for the southern sky to fill some of the faint regions. He originally named it Antlia pneumatica to commemorate the air pump invented by the French physicist Denis Papin. It was later adopted by the International Astronomical Union as one of the 88 modern constellations under the shortened name of Antlia. Main Stars and Deep Sky Objects The Antlia constellation has no bright stars.…
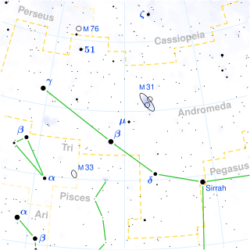
Andromeda Constellation
Andromeda is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. The Andromeda Galaxy is named after the constellation, as it appears within its boundaries.
Astronomy Picture of the Week – Eagle Nebula
From afar, this nebula looks like an eagle, but a closer look however reveals the bright region is actually a window into the center of a larger dark shell of dust, where a whole cluster of new stars is being formed. The Eagle emission nebula, also known as M16 or NGC 6611, lies about 6500 light years away towards the Serpens constellation and spans about 20 light-years. Image credit: T. A. Rector & B. A. Wolpa, NOAO, AURA
Astronomy Picture of the Week – Unusual Spiral Galaxy M66
This is a photo of an unusual spiral galaxy called M66, or NGC 3627, taken by the Hubble Telescope. It lies about 35 million light years from Earth and it spans 100,000 light years. At a first glance, this galaxy looks familiar. Why? Well, because it is similar to our own galaxy, the Milky Way. Both galaxies are spirals. However, what’s really unusual about this one is that it is asymmetric. Usually the force of gravity of a mega black hole (or group of mega black holes) attracts all the stars and interstellar gas in a symmetric pattern. If the mega black hole is not originally in the center of…
Astronomy Picture of the Week – Distant Nebula
This nebula, designated as N 49 or DEM L 190, looks like puffs of smoke or sparks from a fireworks display. It is one of the most distant nebulae ever observed, located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy orbiting the Milky Way. The nebula is the result of a large supernova, whose light should have reached Earth a few thousand years ago.