Astronomy
Embark on an astronomical journey. Explore the cosmos, study celestial objects, and unravel the mysteries of the universe through astronomy's fascinating realm.
Astronomy Picture of the Week – The Cat’s Eye Nebula
This detailed view of the so-called Cat’s Eye Nebula was taken by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. The nebula, formally cataloged as NGC 6543, was one of the first planetary nebulae to be discovered and is one of the most complex. Observations suggest the star ejected its mass in a series of pulses at 1,500-year intervals. This created dust shells, each of which contain as much mass as all of the planets in our solar system combined. These concentric shells make a layered, onion-skin structure around the dying star. Image Credit: NASA, ESA, HEIC, and The Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)
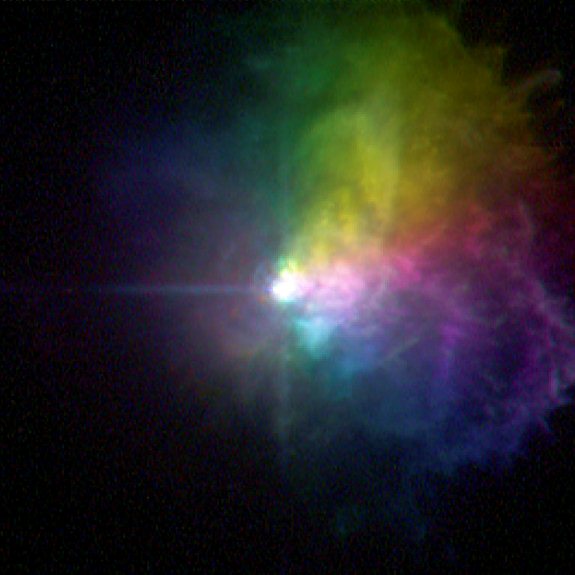
Astronomy Picture of the Week – Polarized Star Light
This picture taken by the Hubble Space Telescope shows the polarized light of the massive star VY Canis Majoris. Image Credit: NASA, ESA, and R. Humphreys (University of Minnesota)
Astronomy Picture of the Week – Interacting Spiral Galaxies NGC 2207 and IC 2163
This near-collision has been caught in a photo by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Two spiral galaxies pass by each other like majestic ships in the night. They are located in the direction of the constellation Canis Major.
Astronomy Picture of the Week – The Colorful Demise of a Sun-Like Star
This image, taken by the Hubble Space Telescope, shows the colorful demise of a Sun-like star. The star is ending its life by casting off its outer layers of gas, which formed a cocoon around the star’s remaining core. Ultraviolet light from the dying star makes the material glow. The burned-out star, called a white dwarf, is the white dot in the center. It is one of the hottest known white dwarfs, with a surface temperature of nearly 200,000 degrees Celsius. The nebula is called NGC 2440 and lies about 4,000 light-years from Earth in the direction of the constellation Puppis. Image credit: NASA, ESA, and K. Noll (STScI)
Astronomy Picture of the Week – NGC 1999 Nebula
This photo of nebula NGC 1999 was taken by the Hubble Space Telescope in December 1999. It is a good example of a reflection nebula. Just like fog around a street lamp, a reflection nebula shines only because a light source illuminates its dust and the nebula does not emit any visible light of its own. The main light source of this nebula is a recently formed star, visible in this photo near the center. This young star is cataloged as V380 Orionis, and its white color is due to its high surface temperature of about 10,000 degrees Celsius (nearly twice that of our own Sun). Its mass is estimated…
Astronomy Picture of the Week – Helix Nebula
This eerie picture captured by the Spitzer Space Telescope shows the Helix Nebula, also known as NGC 7293. It is located 700 light-years away in the constellation of Aquarius. The two light-year diameter shroud of dust and gas around a central white dwarf is the result of the final stages in the evolution of a sun-like star. Dust particles are what makes this cosmic eye look red. Image Credit & Copyright: NASA, JPL-Caltech, Kate Su (Steward Obs., U. Arizona), et al.
Astronomy Picture of the Week – 2010 Lunar Eclipse
Last week, on December 21 we witnessed a lunar eclipse. Below are some pictures of the eclipse: Image Credit & Copyright: Chris Hetlage Image Credit & Copyright: Itahisa N. González (Grupo de Observadores Astronómicos de Tenerife) Credit & Copyright: Jerry Lodriguss (Catching the Light)
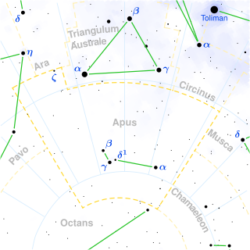
Apus Constellation
Apus is a faint constellation in the southern sky. Its name means “no feet” in Greek and it represents a bird-of-paradise, which were once believed to have no feet. It was one of the twelve constellations created by Petrus Plancius in the late 16th century. The first known depiction of the constellation in a celestial atlas was in Johann Bayer’s Uranometria of 1603. Bird-of-Paradise after which the Apus constellation was named. Credit & Copyright: Roderick Eime. For more constellations see the Constellations Guide.
Astronomy Picture of the Week – Carina Nebula
This is a picture of the Carina Nebula, also known as NGC 3372. It is a huge nebula spanning over 300 light years. The dark shapes you can see in this image are actually clouds of molecular gas and dust so thick they appear opaque.
Introduction to Astronomy – Apparent magnitude
Yesterday I have used the term “apparent magnitude” in my article about the Antlia Constellation. Since some of you may be new to astronomy, I decided to start a new series of articles to introduce you to the topic. Each article of the series will focus on one scientific term used in astronomy. The series will not be a regular one: I will only write an article after using a complicated astronomy term that some of you would need me to explain. Definition The apparent magnitude (noted as m) of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth. Since the apparent brightness…
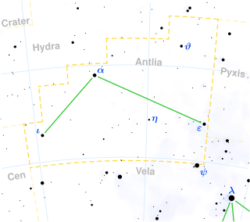
Antlia Constellation
Antlia is a constellation in the southern sky and therefore has been unknown to the ancient Greeks and Romans. Its name means “pump” and it specifically represents an air pump. It was created by the French astronomer Abbé Nicolas Louis de Lacaille, who created fourteen constellations for the southern sky to fill some of the faint regions. He originally named it Antlia pneumatica to commemorate the air pump invented by the French physicist Denis Papin. It was later adopted by the International Astronomical Union as one of the 88 modern constellations under the shortened name of Antlia. Main Stars and Deep Sky Objects The Antlia constellation has no bright stars.…
Astronomy Picture of the Week – Leonid Meteor Shower
Today is the peak of the Leonid meteor shower. It is one of the best meteor showers to watch because it produces an average of 40 meteors per hour during the peak. All meteors seem to come from the Leo constellation, hence it’s name. This picture features a few meteors from the 2001 Leonid meteor shower streaking over Joshua Tree National Park in California, USA. Image credit & copyright: Wally Pacholka (Astropics) & Tony Hallas (Astrophoto) Unfortunately for me the weather is really bad where I live: it is really cloudy with intermittent rain. So I hope some of you had better luck!